
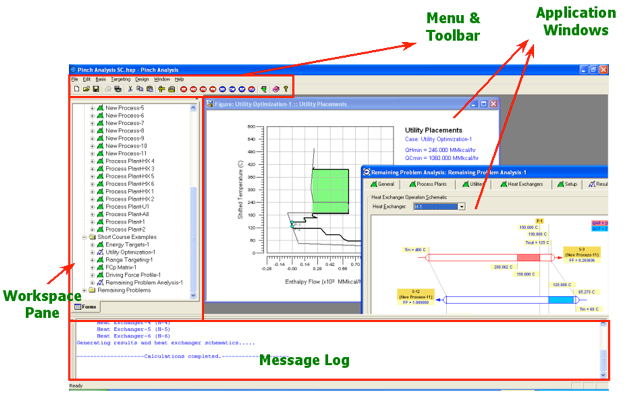
The primary application of Pinch Analysis software is to help process engineers and managers in minimization of wasteful utilization of energy in their process plants, and to analyze and study the energy usage involved. With this software, the user can create stream-based representations of process plants (or parts of process plants) on the site, then analyze and study these process plants through several case studies in order to:
•Evaluate the inherent energy targets and understand/compare existing energy usage
•Quantify energy penalties from current energy usage and identify offending heat exchangers
•Provide insights to generate ideas for improving existing energy usage:
o Ideas for modifying offending heat exchange steps by removing and replacing heat exchangers
o Ideas for modifying existing heat exchangers for improved heat recovery
o Ideas for improved design of the process itself
•Optimize existing utility usage and evaluate usage of other utilities
•Quantify benefits of integrating one or more process units and penalties resulting from area integrity constraints
•Targeting Case Studies
o Energy Targets
o Utility Optimization
o Range Targeting
•Design Case Studies
o FCp Matrix
o Driving Force Analysis
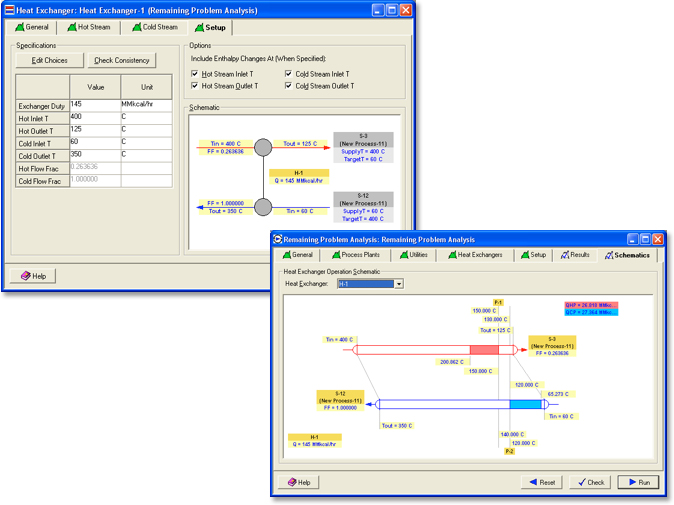
o Remaining Problem Analysis
The first step in pinch analysis (after stream data extraction) is to determine the energy targets, i.e. hot and cold utility usage. The targeting case study functions help the user determine the targets, and additionally determine the optimal utility usage.
Energy Targets
This function enables user to evaluate the inherent energy targets for process plants, and to generate and study the composite and grand composite curves that for the process. The energy targets quantify the best we can achieve and provide a number to aim at. This functionality can also quantify the benefits of integrating one or more process units and penalties resulting from area integrity constraints.
Utility Optimization
With this functionality the user can (a) determine optimal utility placements using the grand composite curve (b) optimize existing utility usage in process plants and evaluate the opportunities of and benefits from using other/additional utilities, and (c) create and study shifted balanced composite curves and balanced grand composite curve.
Range Targeting
The choice of an optimum plant-wide ¦¤Tmin can be determined by range targeting. The objective is to quantify how energy targets change with ¦¤Tmin, as also utility placements, optimal usage, and optimal costs change with ¦¤Tmin.
After determining the energy targets and appropriate utility levels, the next task is to design a new network or to determine the efficacy of the current heat exchanger network. The design case studies assist the user in this determination.
FCp Matrix
This functionality helps the user select streams that can be matched with each other at the pinch temperatures (on either side of the pinch), when designing modifications to the existing exchangers/heat exchange steps.
Driving Force Profiles
The use of this functionality is (a) to study the inherent driving force as a function of hot and/or cold composite temperatures, (b) to select the exchanger duty for streams which are matched with each other when designing modifications to the existing exchangers/heat exchange steps, and (c) to compare the operation of existing heat exchangers to the inherent driving force profile.
Driving Force Profiles
This case study is particularly useful for existing design study because it enables the user to identify the energy penalty from current energy usage and to identify and rank the offending heat exchangers, i.e. to visualize heat exchanger operation and the cross-pinch energy transfers (if any).
In addition to the core functionality, the Pinch Analysis software provides several special features to help the user get the best out of the software and to practice the technology. Some of the important special features are discussed here:
•Intuitive & Hierarchical Organization
•Flexibility & Focus on Insights ¡ª the software allows user to create stream-based representations of multiple process plants in any workspace, even multiple representations of the same process plant
•Handling Constant Temperature Enthalpy Changes ¡ª user can input data for streams that represent constant temperature enthalpy changes without any artificial modification to the supply or target temperatures
•Defining a Custom Utility ¡ª In addition to standard utilities such as cooling water, steam use and generation, hot oil, refrigeration, use can generate a custom utility with its own definitions.
•Water & Steam Properties ¡ª the software provides direct access to the thermodynamic properties of water and steam. The parameters and methods for calculating these properties are based on the IAPWS Industrial Formulation 1997 of the ASME steam tables (IAPWS-IF97).
Total Site Energy Management along with Pinch Analysis together addresses the two important problems that comprise the Total Site Analysis. There are great benefits through the integrated use of these two as, among others, the user can study:
•The interaction between the supply and demand of steam
•The optimum selection of the site-wide and local steam header levels
•The impact of plant capacity on the total site utility consumptions

Copyright of ClearWaterBay (Beijing) Technology |